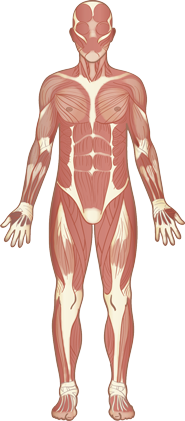
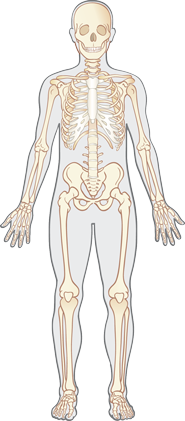
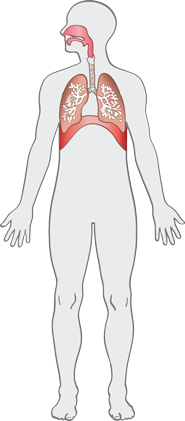
Click on an organ system below to view its components.
Organ systems are groups of organs that work together to perform complex functions.
An organ is a recognizable structure. It is composed of different kinds of tissues that work together to take care of specific functions.
Tissues are made of lots of related kinds of cells working together to perform specific functions. Tissues exist only in multicellular organisms.
Cells working together make up tissues.
Skeletal muscles are the only voluntary muscles in the muscular system that allow movement and control posture. Skeletal muscles are connected to bones.
The skeletal system provides structure, shape, and protection for the soft tissues of the body. It also allows movement. Blood cells are produced in long bones.
The respiratory system provides oxygen for the body's cells and disposes of carbon dioxide and water.
The nervous system senses the environment. It controls all voluntary and involuntary actions in the body.
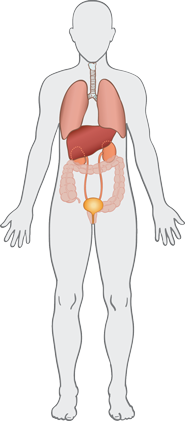
The excretory system is responsible for getting rid of bodily waste. The part of the excretory system that rids the body of liquid waste is the urinary system.
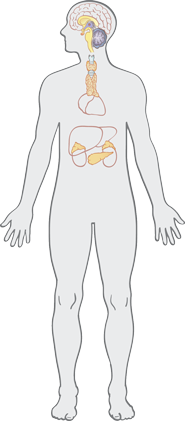
The endocrine system includes all of the glands in the body and the hormones they produce. Hormones help regulate the functions of most organs in the body.
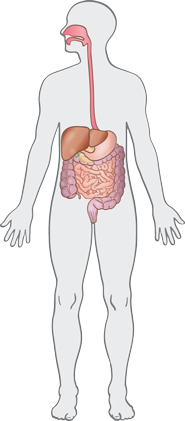
The digestive system breaks down the food we eat into small molecules which the body will use. It consists of one long tube, food entering at the mouth, and leftover waste exiting from the anus.
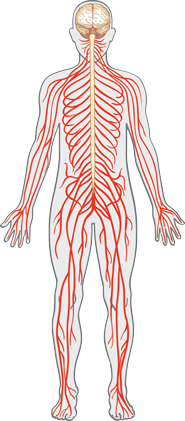
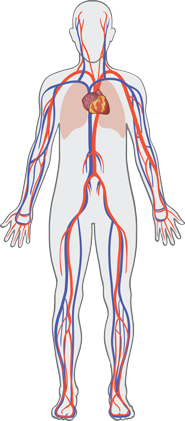
The circulatory system transports substances to the cells in the human body. The cardiovascular system is part of the circulatory system and is responsible for delivering oxygen, nutrient molecules, and hormones to the cells. It also transports cellular waste products such as carbon dioxide and water away for disposal.
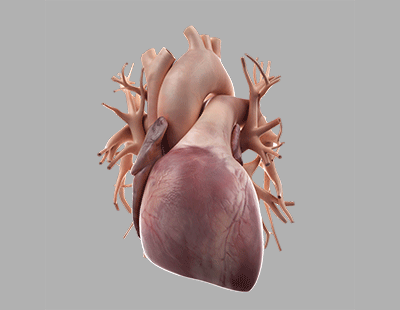
Heart
The heart is a muscular pump that pumps blood throughout the body.
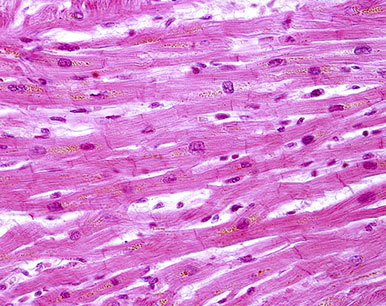
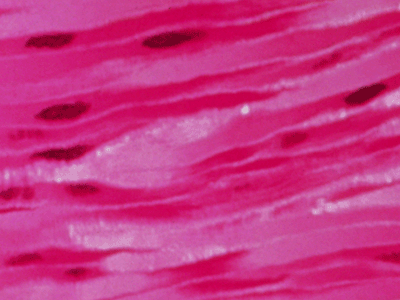
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Found only in the heart. Unlike other muscle tissue in the body, cardiac muscle never stops working, contracting to pump blood to the rest of the body.
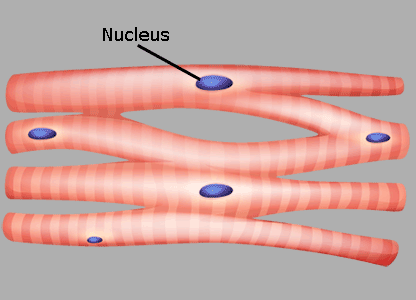
Cardiac Muscle Cells
Found only in the heart. These cells have a branched shape that allows them to be in contact with three or four other muscle cells. Together, they form an interlocking network of tissue.
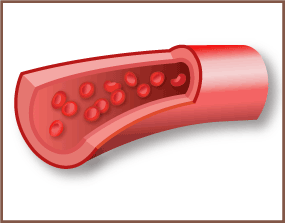
Blood Vessels
There are three types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
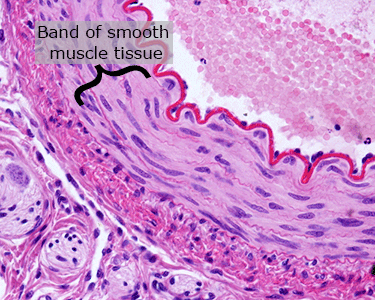
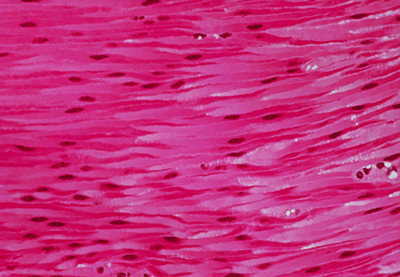
Smooth Muscle Tissue
The walls of the veins and arteries are made of smooth muscle tissue. The band of smooth muscle is thick in arteries. It expands and contracts to help pump blood away from the heart. The walls of veins are thin; they do not need to be as strong and elastic as artery walls.
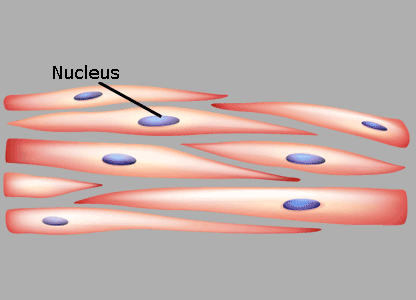
Smooth Muscle Cells
Smooth muscle cells are not branched or interconnected. Each cell works together with others to produce contractions.
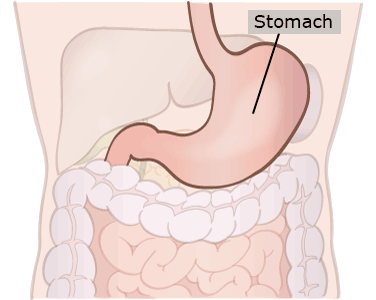
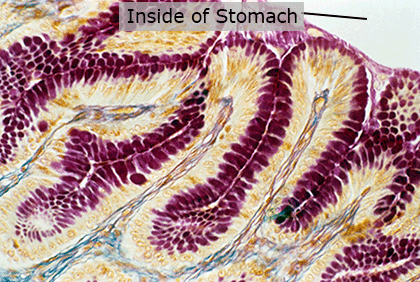
Stomach
The stomach produces acid and other chemicals and mechanically churns food to break it down. It releases partially digested food to the small intestine a little bit at a time.
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Smooth muscle tissue is one of the layers of tissue in the stomach wall. It is made of groups of cells that can contract and relax. The contraction and relaxation is controlled by the brain without your thinking about it.
Smooth Muscle Cells
Smooth muscle cells are not branched or interconnected. Each cell works together with others to produce contractions.
Epithelial Mucosa Tissue
Epithelial tissue is made of many cells closely packed together. This tissue is the inner lining of the stomach. It produces acid to digest food and mucus which protects the other tissues from the acid in the stomach.
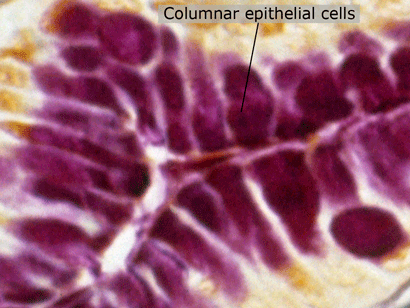
Columnar Epithelial Cells
Columnar epithelial cells release acid into the stomach.
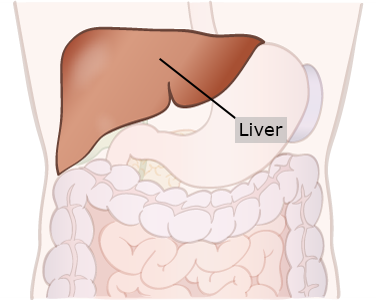
Liver
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body. It filters toxins (poisons) out of the blood, absorbs sugar, and produces parts of the blood.
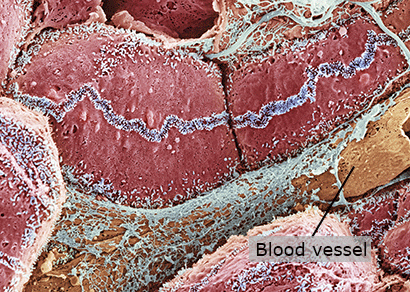
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is made of many cells closely packed together. This kind of tissue lines most of the inner linings of organs. The cells that make up most of the liver's epithelial tissue are squarish in shape.
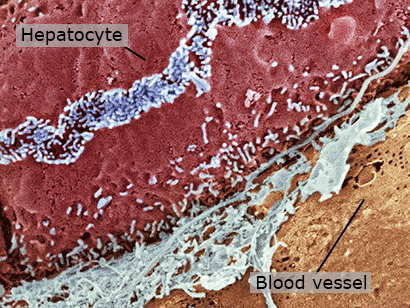
Hepatocytes
Hepatocytes are epithelial cells that make up almost 80% of the mass of the liver. They perform most of the liver's functions including manufacture and storage of proteins and formation of bile.
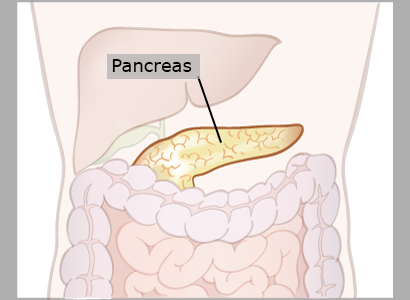
Pancreas
The pancreas makes the hormones insulin and glucagon which regulate the level of sugar in the cells.
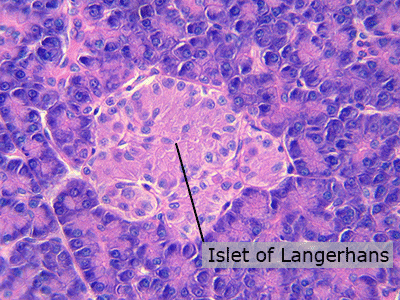
Islets of Langerhans
The islets of Langerhans are groups of cells in the pancreas. They produce the hormone insulin which lowers blood sugar levels and the hormone glucagon which raises blood sugar levels.
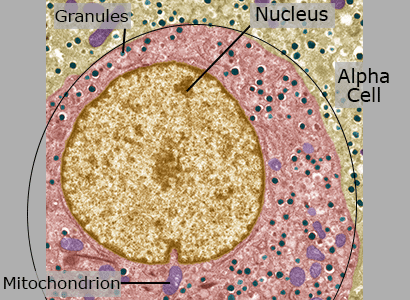
Alpha Cells
Alpha cells are found in the islets of Langerhans. They produce glucagon which raises glood sugar levels in the blood.
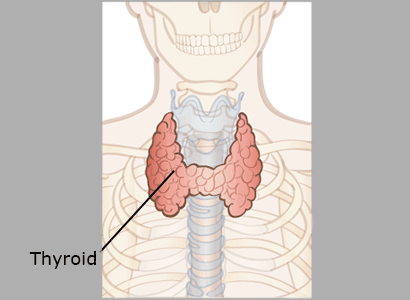
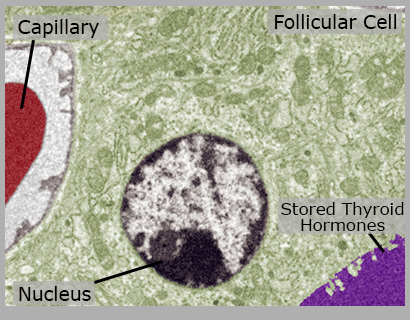
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland controls the rate at which the body produces energy.
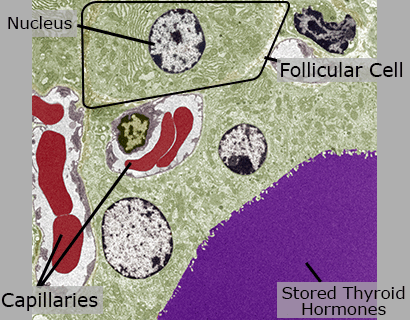
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is made of many cells closely packed together. This tissue is made of cells that surround stored thyroid hormones.
Follicular Cells
Follicular cells are epithelial cells in the thyroid that produce thyroid hormones.
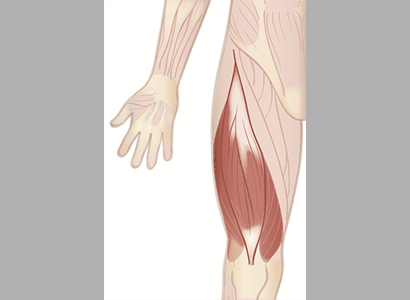
Quadriceps
The quadriceps is the set of very strong thigh muscles.
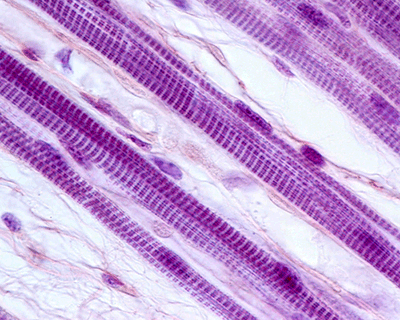
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Every physical action you choose to do requires skeletal muscle tissue.
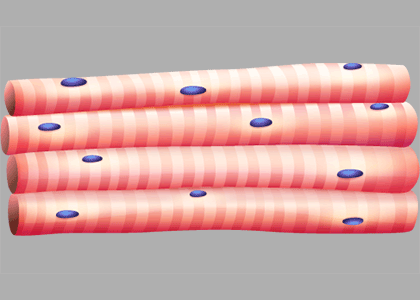
Skeletal Muscle Cells
Skeletal muscle cells form when many smaller cells group together to form long, straight fibers with neveral nuclei. These fibers are very strong.
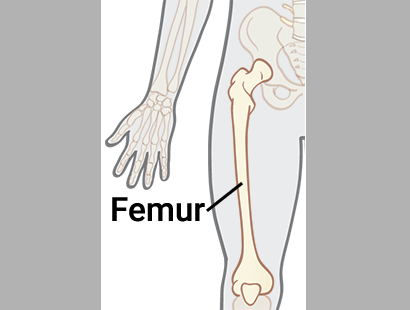
Femur
The femur is a complex long bone that connects the hip to the knee.
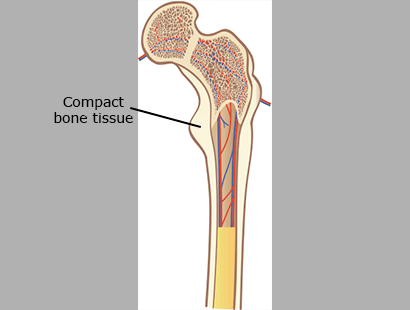
Compact Bone Tissue
Compact bone tissue is the dense extremely hard outer layer of bone. It makes up 80% of bone tissue and supports the weight of the body. It appears solid but is filled with many tiny passages for blood vessels and nerves.
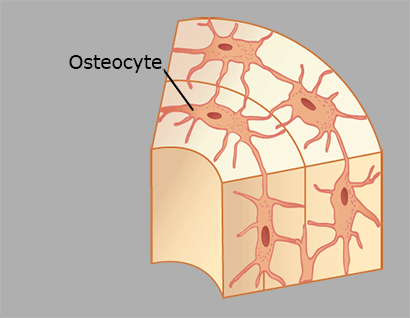
Osteocytes
Osteocytes are arranged in rings around canals in compact bone tissue.
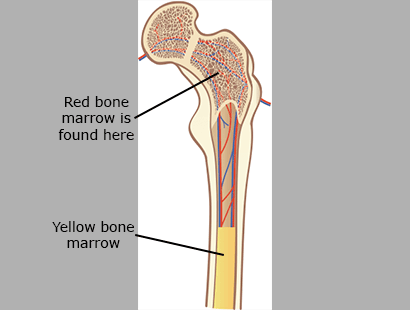
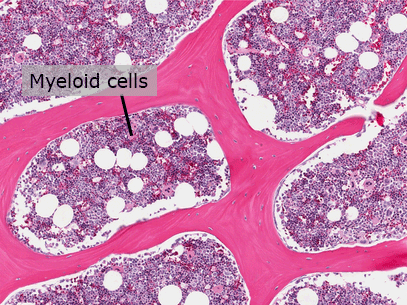
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a soft tissue found inside bones. Red bone marrow produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Yellow bone marrow is made mostly of fat and is found in long bones such as the femur. It does not make blood cells.
Myeloid Cells
Myeloid cells in red bone marrow produce white blood cells that fight infection.
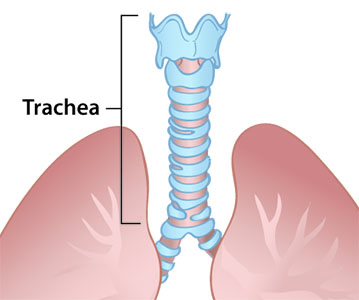
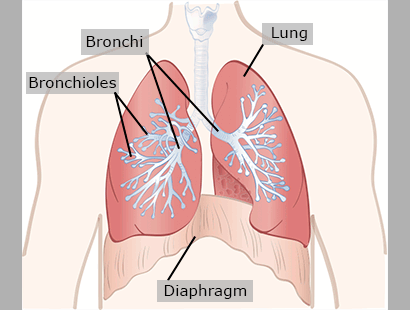
Trachea
The trachea is also called the windpipe. It is a hollow tube that air travels through to the lungs.
Mucosa Epithelial Tissue (lines the inside of the trachea)
Mucosa epithelial tissue lines the inside of the trachea. It secretes mucous which traps particles and bacteria.
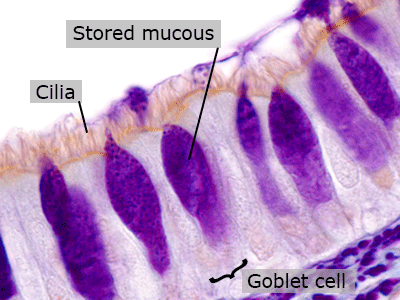
Goblet Cells
Goblet cells are epithelial cells that secrete mucous to protect the lining of the trachea. Some cells have little hairs called cilia that propel the mucous (and any trapped particles) away from the lungs.
Lungs
The lungs are the main organs in the respiratory system. They are responsible for gas exchange.
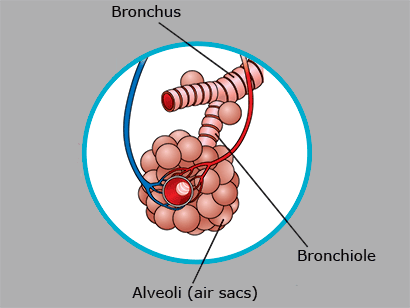
Alveoli (Epithelial Tissue)
Alveoli are tiny air sacs made of spongy epithelial tissue found at the end of bronchioles. They are surrounded by capillaries which are tiny blood vessels. Gases such as oxygen pass from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries. Carbon dioxide passes from the capillaries to the alveoli and is exhaled.
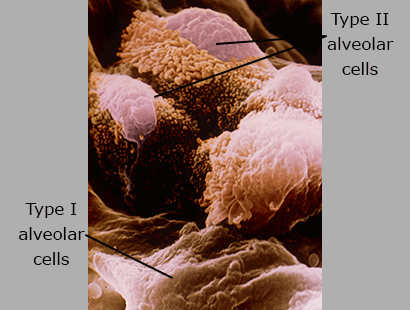
Alveolar (Epithelial) Cells
Carbon dioxide and oxygen pass through the type I alveolar cells to the bloodstream. The type II alveolar cells secrete a substance that keeps the air sac from collapsing.
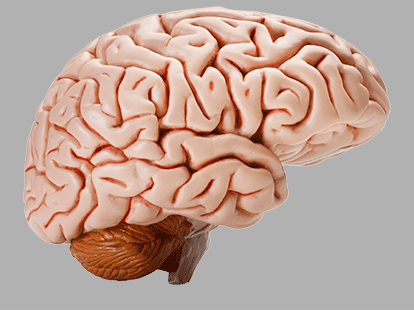
Brain
The brain is the principal processing organ in the human body. It is responsible for thought, muscle control, decision-making, learning, and memory.
Neural Tissue
The brain's neural tissue is folded upon itself so that the largest amount of tissue possible can fit within the skull. It is is made up of two types of cells: neurons and glial cells.
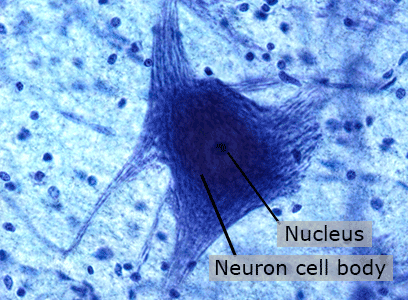
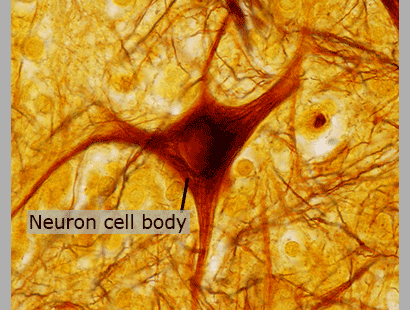
Neurons
Neurons are responsible for all of the communication and processing within the brain.
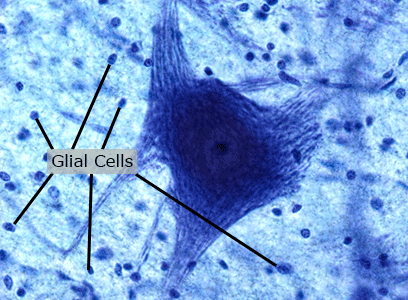
Glial cells (Neuroglia)
Glial cells are neural cells that support and protect neurons.
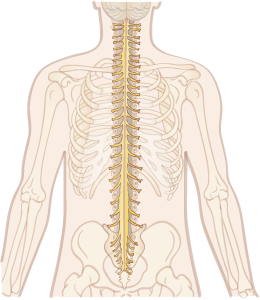
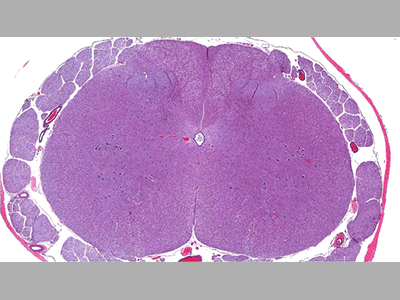
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord provides 2-way communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
Neural Tissue
The neural tissue of the spinal cord is made up of neurons that form complex networks.
Neurons
Neurons in the spinal cord carry messages either toward the brain or from the brain.
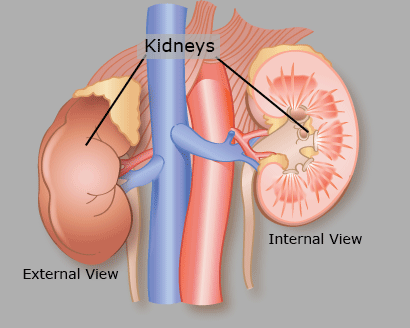
Kidney
The kidney removes wastes that contain nitrogen, salts, and excess water, creating urine.
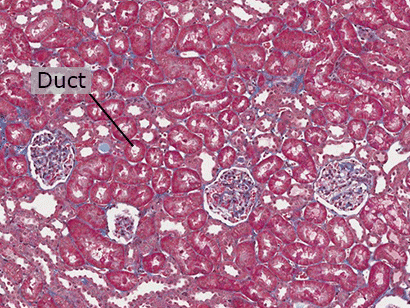
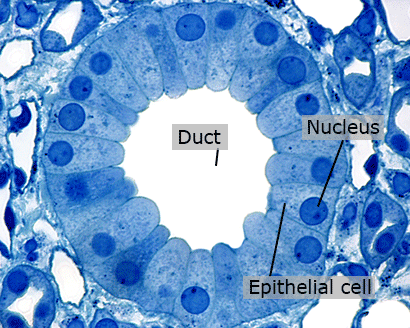
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is made of many cells closely packed together. This kind of tissue lines most of the inner linings of organs. In the kidneys, epithelial cells make up collecting ducts which collect fluids that will be excreted out of the body.
Epithelial Cells
The cells that line the collecting ducts in the kidney tissue are columnar epithelial cells.
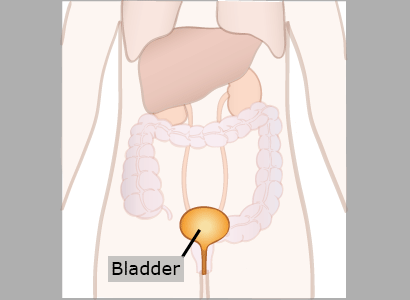
Bladder
The bladder stores urine until it is excreted. It is one of the most elastic organs in the body.
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Smooth muscle tissue is one of the layers of tissue in the bladder. It is made of groups of cells that can contract and relax. The contraction and relaxation is controlled by the brain without your thinking about it. However, you can usually control the release of urine.
Smooth Muscle Cells
Smooth muscle cells are not branched or interconnected. Each cell works together with others to produce contractions.